Alexander Z
Student
Fragen
Resümees
Videos
Audios
Where does the spinal cord typically end in the vertebral column?
August 24, 2024
In patients with peripheral neuropathy, which nerve lesion is commonly associated with foot drop and loss of ankle jerk reflex?
August 24, 2024
Which condition can cause wasting and weakness of the quadriceps, along with diminution or loss of the knee jerk?
August 24, 2024
What presenting symptom might be associated with adult-onset diabetes mellitus?
August 24, 2024
To differentiate between a femoral nerve lesion and an L2/3/4 root (or plexus) lesion, which muscle should you test?
August 24, 2024
Which conditions are characterized by dissociated sensory loss, where the patient can feel the lightest touch but cannot distinguish one end of a pin from the other?
August 24, 2024
In peripheral neuropathies and common peroneal nerve lesions, which muscle often shows wasting?
August 24, 2024
In a patient with sciatica, which motor sign may be the only indication of an L5 root lesion?
August 24, 2024
Which clinical feature is characteristic of hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP)?
August 24, 2024
Which condition is characterized by a shuffling gait with small steps and loss of arm swing, often seen in patients with a normal base?
August 24, 2024
Which of the following features should make you consider a rotator cuff injury rather than an axillary nerve lesion?
August 3, 2024
When should you test for weakness of neck flexion or extension in a patient?
August 3, 2024
Which of the following methods is correct for detecting weakness in the brachioradialis muscle?
August 3, 2024
Which of the following is a correct method to determine if shoulder abduction weakness is due to the serratus anterior or trapezius muscles?
August 3, 2024
Which muscle is crucial to test in a suspected case of radial nerve palsy?
August 3, 2024
Why is it almost impossible to abduct the fingers when they are flexed at the metacarpophalangeal joints, especially in the context of wrist drop?
August 3, 2024
When should myasthenia gravis be considered as a potential diagnosis in a patient with eye movement weakness?
August 3, 2024
Ptosis accompanied by weakness of the orbicularis oculi muscle, which improves with rest but worsens with activity, is most likely indicative of which condition?
August 3, 2024
Pupillary inequality due to an oculomotor palsy is most obvious in which type of lighting condition?
August 3, 2024
Complete ptosis, where the pupil is covered by the lid, is unlikely to be due to which of the following conditions?
Juli 31, 2024
Q 2.21. Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis
Mai 19, 2024
Q 1.28. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Syndromes of Damage
Mai 19, 2024

Q 1.18. Syndromes of Parietal Lobe Damage
Mai 18, 2024

Q 1.15. Higher Cortical Functions. Gnosis and Agnosia. Praxis and Apraxia.
Mai 13, 2024
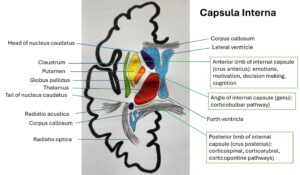
Q 1.21. Internal Capsule Syndromes. Thalamic syndrome.
Mai 13, 2024

Q 1.27. Autonomic nervous system: anatomy and physiology. Impairment syndromes. Examination methods. Orthostatic intolerance. Horner syndrome.
Mai 2, 2024
Q 1.17. Syndromes of Frontal Lobe Damage
April 24, 2024
Q 1.19. Temporal Lobe Syndromes
April 24, 2024
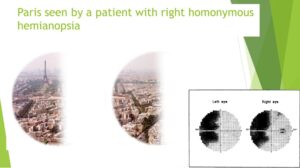
Q 1.20 Syndromes of Occipital Lobe Damage
April 24, 2024
Q 1.23. Brainstem Syndromes: Pons
April 24, 2024

Q 1.24. Brainstem Syndromes: Mesencephalon
April 23, 2024
Q 1.25. Spinal Cord: Anatomy, Physiology, and Blood Supply
April 7, 2024
Q 1.22. Brainstem Vascular Syndromes: Medulla Oblongata
April 7, 2024
Q 1.29. Syndrome of meningeal irritation. Examination methods. Syndrome of increased intracranial pressure.
April 7, 2024
Q 1.31. Anatomy and Physiology of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF). CSF Syndromes.
März 31, 2024
Q 2.6. Polyneuritis and Polyneuropathies. Toxic and Deficiency Neuropathies.
März 31, 2024
No videos found
Question 1: Peripheral Nervous System Disorders. Classification. Neuralgia, mononeuritis, plexitis. Treatment.
Radiographic Evaluation of the Cranium
Februar 2, 2024