Dr. Petya Stefanova
Teacher
Assistant at the Faculty of Medicine at Sofia University and resident physician in Neurology at Sofiamed University Hospital.
Fragen
Resümees
Videos
Audios
For which disease is atherosclerosis considered a serious risk factor?
August 22, 2023
EMG findings in myasthenia often reveal characteristic patterns indicative of muscle weakness.
August 22, 2023
EMG findings in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) commonly exhibit signs of denervation and spontaneous muscle activity.
August 22, 2023
What are the main vessels participating in cerebral circulation?
August 22, 2023
EMG findings in discal herniation typically show abnormal patterns indicative of muscle weakness.
August 22, 2023
From which major arterial vessel does the right common carotid artery originate?
August 22, 2023
What are common EMG findings in diabetic polyneuropathy?
August 22, 2023
What is the key anatomical difference between the external and internal carotid arteries?
August 22, 2023
Which of the vessels arise from the external carotid artery?
August 22, 2023
What accurately describes the anatomy of the vertebral artery?
August 22, 2023
What accurately describes the anatomy of the Circle of Willis?
August 22, 2023
What factors contribute to cerebral blood pressure regulation?
August 22, 2023
What is the routinely most commonly used test for evaluating atherosclerosis in the extracranial vessels?
August 22, 2023
What is considered the golden standard for visualizing intracranial vascular pathology?
August 22, 2023
Clinicians should be mindful that anatomical variations and hypoplasia are common occurrences in the vertebral artery. These variations may have clinical significance and should be considered in assessments, particularly in vascular imaging.
August 22, 2023
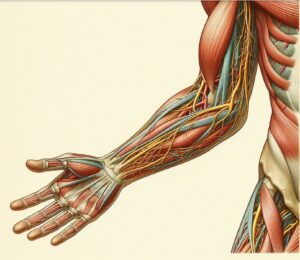
Q 2.1. Peripheral Nervous System Disorders. Classification. Neuralgia, mononeuritis, plexitis. Treatment.
Februar 2, 2024
No videos found
Fake Smiles, Real Damage: How Digital Joy Breeds Fear and Anger
Mai 3, 2025
Understanding Neuropsychological Evaluations: What to Expect
Februar 25, 2025
Невропсихологическо изследване – индикации, провеждане и резултати
Februar 24, 2025
Невропсихологическо изследване – индикации, провеждане и резултати
Februar 24, 2025