Dr. Petya Stefanova
Teacher
Assistant at the Faculty of Medicine at Sofia University and resident physician in Neurology at Sofiamed University Hospital.
Въпроси
Резюмета
Видеа
Аудио
What is a key difference between the pyramidal and extrapyramidal pathways in the central nervous system?
октомври 31, 2023
Кои симптоми насочват към засягане на екстрапирамидната система?
октомври 31, 2023
What are the primary functions of the extrapyramidal system in the central nervous system?
октомври 31, 2023
What does the term “aphasia” refer to?
октомври 31, 2023
Какво означава терминът “афазия”?
октомври 31, 2023
Is muscle atrophy typically observed as a symptom of lower or upper motor neuron lesions?
октомври 18, 2023
Мускулна атрофия се наблюдава при:
октомври 18, 2023
If a patient has an absent knee reflex on their right leg, what could this symptom potentially indicate?
октомври 18, 2023
Липсващ коленен рефлекс в ляво може да е симптом при:
октомври 18, 2023
Pathological reflexes are observed in:
октомври 18, 2023
Наличие на патологични рефлекси е характерно за:
октомври 18, 2023
What is the clinical interpretation of a suction positive reflex in elderly?
октомври 18, 2023
Каква е клиничната интерпретация на положителен палмо-ментален рефлекс?
октомври 18, 2023
What is a key difference between peripheral and central facial nerve palsy?
октомври 13, 2023
What is the primary function of the olfactory nerve (CN I)?
октомври 13, 2023
What is the vision field defect as shown on the picture?
октомври 13, 2023
What is the visual defect shown on the picture?
октомври 13, 2023
What is the most common reason for the visual defect shown on the picture?
октомври 13, 2023
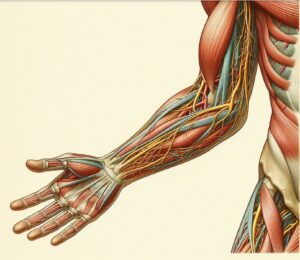
Q 2.1. Peripheral Nervous System Disorders. Classification. Neuralgia, mononeuritis, plexitis. Treatment.
февруари 2, 2024
Fake Smiles, Real Damage: How Digital Joy Breeds Fear and Anger
май 3, 2025
Understanding Neuropsychological Evaluations: What to Expect
февруари 25, 2025
Невропсихологическо изследване – индикации, провеждане и резултати
февруари 24, 2025
Невропсихологическо изследване – индикации, провеждане и резултати
февруари 24, 2025